What is the profit formula?
Calculating profit for a business involves using the profit formula, which is revenue minus expenses.
As a small business owner, you’re likely always looking for ways to boost your income. Whether that’s by increasing sales, eliminating redundancies, or decreasing expenses, you should be looking for the next big cost-saving measure to free up valuable cash flow.
When analyzing the reports from your accounting software to see if your business is on track, you’ll want to use the profit formula. This will show you your profit (aka bottom line). Let’s dive into some of the best ways to calculate profit:
How to calculate profit

Much like a fingerprint, no two businesses are the same. No two companies will track business expenses same either. The good news is that the profit equation is fairly straightforward and only requires punching in some variables. The profit formula is:
Profit = revenue – expenses
Steps to calculate profit
Step 1: Determine revenue
Revenue is all the money your business earns from sales. This includes any income generated from selling products or services.
Formula: Revenue = Total Sales
Step 2: Calculate expenses
Expenses include everything your business spends money on, from supplies and materials to rent, utilities, and even salaries. Add up all the costs your business incurs.
Formula: Expenses = Total Costs (supplies, rent, utilities, etc.)
Step 3: Subtract expenses from revenue
To find your profit, subtract your total expenses from your total revenue.
Formula: Profit = Revenue – Expenses
Profit formula example
Business owners use the profit formula to see how much income they generate. For example, let’s say you have a boot store that generates $100,000 in annual revenue. Once you take out the cost of the leather, you have $80,000 (this is your gross profit).
Next, you take out your operating costs and other expenses, such as the salary of your part-time cashier, the rent, taxes, and utilities. This comes out to $35,000. Now take the $80,000 and subtract the $35,000. This leaves you with a profit of $45,000.
You can also use the equation for profit to look at the profitability of certain products. For example, your boot store may offer three different product types and find that, although overall company sales are steady, your leather boot sales have declined in recent months. After figuring out the profit for that particular product line, you may decide to discontinue the product.
Once you have the profit formula down, you can use other profit formulas and financial KPIs to see how efficiently you use your resources.
Different types of profit formulas
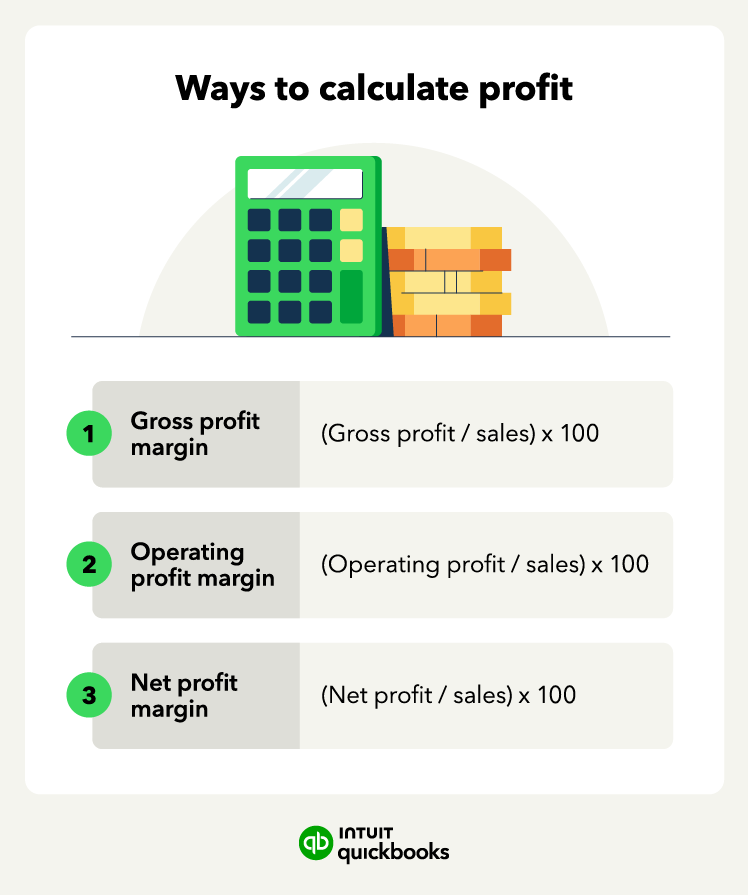
When calculating profitability, businesses often look at profit margins. Profit margins are percentages that help measure the profitability of a business and come in different forms, such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin.
How to find gross profit margin
The gross profit margin equation typically helps determine the profit margin of a singular product or service, not of an organization as a whole. The gross profit margin formula is:
Gross profit margin = gross profit / sales x 100
Steps to calculate gross profit margin
Step 1: Determine gross profit
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your revenue. COGS includes expenses like raw materials, labor, and production costs.
Formula: Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
Step 2: Divide gross profit by sales (revenue)
To find the gross profit margin, divide your gross profit by your sales revenue. This shows the percentage of each dollar of revenue that is gross profit.
Formula: Gross Profit Margin = Gross Profit / Revenue
Step 3: Multiply by 100
Multiply the result from Step 2 by 100 to convert the gross profit margin into a percentage.
Formula: Gross Profit Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100
Gross profit margin example
If you sell a leather belt at your boot store for $25 and it costs $20 to produce, your gross profit is $5.
Gross profit margin = ($5 / $25) x 100 = 20%. This means 20% of your sales go back into your pocket as profit.
This method can be applied to individual products or services to understand how much of your revenue is actual profit.FYI: Each industry generally has its own average profit margins due to the differences in costs and materials needed for the different products and services across various industries.
How to find operating profit margin
The operating profit indicates how much money the company makes from its core operations after accounting for all operating costs and expenses. The operating profit margin formula is:
Operating profit margin = operating profit / revenue x 100
Steps to calculate operating profit margin
Step 1: Calculate gross profit
Start by determining your gross profit. This is your total revenue minus your cost of goods sold (COGS), which includes the direct costs of producing your products.
Step 2: Subtract operating expenses
Once you have your gross profit, subtract your operating expenses. Operating expenses include things like administrative costs, marketing expenses, and overhead.
Formula: Operating Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Step 3: Divide operating profit by revenue
To find your operating profit margin, divide your operating profit by your total revenue. This shows what percentage of revenue is left after covering all operating costs.
Formula: Operating Profit Margin = Operating Profit / Revenue
Step 4: Multiply by 100
Multiply the result from Step 3 by 100 to convert it into a percentage.
Formula: Operating Profit Margin (%) = (Operating Profit / Revenue) x 100
H2: Operating profit margin example
If your boot wholesaler generates $10 million in sales and has $5 million in operating expenses, your operating profit is $5 million.
Operating profit margin = ($5 million / $10 million) x 100 = 50%. This means 50% of your revenue is retained as operating profit after covering all operating expenses.
How to find net profit margin
Net profit margin determines an entire company’s profit margin—it takes into account all revenue and expenses. The formula to find net profit margin is:
Net profit margin = net profit / revenue x 100
Run your business with confidence
Get help and guidance when you need it from real bookkeeping experts at Eric Buchholz Bookkeeping… Get Started right HERE!
Steps to calculate net profit margin
Step 1: Start with operating profit
Begin with your operating profit—the profit remaining after subtracting all operating expenses from revenue. This figure gives you the income before considering taxes, interest, or other non-operating expenses.
Step 2: Subtract all other expenses
From your operating profit, subtract other expenses such as taxes, interest, and any one-time costs. These additional expenses are deducted to arrive at your net profit (aka net income).
Formula: Net Profit = Operating Profit – Taxes – Interest – Other Expenses
Step 3: Divide net profit by revenue
To determine the net profit margin, divide your net profit by your total revenue. This percentage reflects how much of your revenue is actual profit after covering all expenses.
Formula: Net Profit Margin = Net Profit / Revenue
Step 4: Multiply by 100
Multiply the result by 100 to convert it into a percentage.
Formula: Net Profit Margin (%) = (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100
Net profit margin example
If your operating profit is $5 million and you have $1 million in other expenses, your net profit is $4 million.
Net profit margin = ($4 million / $10 million) x 100 = 40%. This means 40% of your total revenue is left as net profit after all costs and expenses are accounted for.FYI: Net profit margin often uncovers a large expense or group of expenses that are hampering company profits. It could also reveal that market demand will support a price increase.
Common mistakes in profit margin calculation to avoid
Calculating your profit margin is a vital part of running a successful business, but there are some common mistakes that can throw off your numbers. Avoiding these errors will help you get a clearer and more precise picture of your financial health. Here are some common pitfalls and how to prevent them.
Ignoring indirect costs
It’s easy to forget about indirect costs—things like rent, utilities, and salaries that aren’t tied to producing a specific product or service. Failing to factor in these expenses when calculating profit margin will result in inflated numbers.
How to avoid this: Make sure to include both direct and indirect costs to get an accurate measure of your profitability.
Confusing markup with profit margin
A frequent mistake is mixing up markup with profit margin. While they both have to do with the cost-revenue relationship, they measure different things. Markup is how much more you charge over the cost of a product, while profit margin is the percentage of revenue left after covering costs. Confusing the two can lead to pricing errors and affect your bottom line.
How to avoid this: Be sure to calculate profit margin using this formula:
Profit Margin = (Revenue – Cost) / Revenue
Using gross profit instead of net profit
Using gross profit instead of net profit to calculate margins will give you an incomplete view of your profitability. Gross profit only takes into account sales minus the cost of goods sold (COGS), while net profit factors in all expenses, including taxes and overhead.
How to avoid this: When calculating your profit margin, be sure to account for all expenses. This includes taxes and overhead, not just the cost of goods sold.
Forgetting to update costs
Business expenses can fluctuate frequently. Whether you’re paying more for materials or labor, failing to update your costs accordingly can skew your profit margin calculation.
How to avoid this: Stay on top of these changes to ensure you’re always working with up-to-date numbers so you can calculate accurate profit margins.
Incorrectly allocating expenses
Sometimes, business owners misallocate expenses. For example, mixing personal expenses with business costs or incorrectly categorizing expenses can lead to inaccurate margins.
How to avoid this: Make sure your expenses are properly categorized so that your financial reports are reliable.
What’s a good profit?
Now that you have your profit margin in hand, you might be wondering—what is a good profit margin for your business? To start, consider these two factors when assessing your profits:
Your industry
Not every industry has the same profit margins. For example, an accounting firm can have a profit margin of nearly 20%, while a tech consulting firm may have one of around 10%, with both businesses still being successful in their niche.
Age of your business
A newer business may have a higher or lower profit margin than the average. It might be lower if the company sells at lower prices to attract customers.
Other factors that affect profit margin include company size, location, production processes, and target audience.
Look at your business on its own, then compare yourself to others in your industry. Be sure to consider how established most businesses in your industry are before you jump to any conclusions.
Best practices: What to do with your profit formula
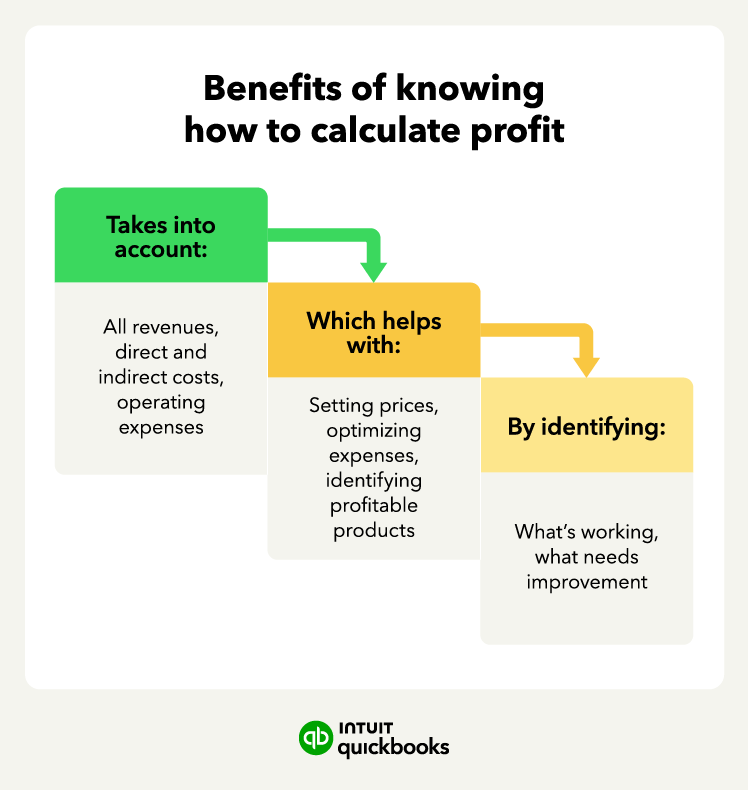
To get an accurate profit formula calculation, a company must include every expense as part of the total. This includes things like payroll, utilities, inventory management costs, administrative costs, and shipping. Every line item in your accounting ledger that is an expense must factor into your total expenses line item.
Similarly, you must gather all revenue sources as well. Don’t forget nontraditional revenue sources, such as transaction fees or maintenance contracts.Chances are you have a much clearer picture of your revenue streams than your expenses, but you should still be careful to avoid miscalculations for each amount.
Once you have your profit calculations, it’s time to analyze them and create a strategy. This may include:
Exploring the options of increasing production or introducing new products
If your profit margin is good, this might be the perfect time to explore growth opportunities. Consider how more production would affect your profit margins. How much would your costs increase? And could you maintain the same profit margin, or would there be a decline?
Strategizing on ways to improve your profits
If your profits and margins need improvement, it could be time for other changes. You can start by examining ways to increase profit by decreasing expenses. Things like renegotiating contracts, shifting production schedules, or hiring new employees can all affect your revenue and expenses.
In all instances, taking a long look at any sweeping changes that might result from tweaking your profits is a good idea.
For example, although a particular product might not be as profitable as it once was, what are the ramifications of doing away with it entirely? Consider your customers, your employees, and your company’s brand when making any kind of change.
Streamline your accounting and save time
Using the profit formula to assess your business is something every business owner should do regularly—at least monthly. In particular, the net profit margin is a strong measure of your company’s profitability, looking at how much of your revenue you keep after all expenses.
This process gets much easier if you have accounting software like QuickBooks that makes financial reporting easier.
Ready to get started?
Take routine bookkeeping off your never-ending to-do list with the help of a certified professional. At Eric Buchholz Bookkeeping, we can help ensure that your business’s books close every month, and you’re primed for tax season. Our expert certified QuickBooks ProAdvisors have over 25 years of experience working with small business bookkeeping across various industries.
Whether you’re learning what a good profit margin should be for your business, or strategizing on ways to improve your profits, Eric Buchholz Bookkeeping can guide you down the right path. Schedule your FREE phone consultation today!… Simply CLICK HERE.





